Exploring the Dynamic Evolution of Ecosystem Services in the Aral Sea Basin: A Fascinating Study
The ‚ÄčAral Sea Basin has long been the focus ‚Ā§of extensive research due to its‚Ā§ unique ‚ĀĘposition as a‚Äč critical‚ĀĘ ecosystem in Central‚ĀĘ Asia. ‚ÄčOver the decades, the region has experienced significant environmental ‚Ā§and socio-economic changes, leading to a dynamic evolution of ecosystem services. With the decline of the Aral Sea itself, researchers have been exploring the complex interplay of ‚Äčecological processes‚Äć and human activities, attempting ‚ÄĆto understand ‚ÄĆand manage the changes in ecosystem services within the basin.
The Aral ‚ÄĆSea Basin‚ÄĆ is known for its once-thriving fishing industry, agriculture, and diverse biodiversity. However, the ‚Äćdiversion‚Äć of‚Ā§ water from the two main rivers feeding the Aral Sea, the Amu ‚ĀĘDarya and Syr Darya, for irrigation purposes has led to a ‚ÄĆsevere ‚Äćreduction ‚ÄĆin the sea’s ‚ÄĆwater volume and an increase in salinity. As a result, the ecosystem services ‚Ā£in the ‚Ā£region have undergone a profound transformation. Let’s delve into the ‚Äćfascinating study of the dynamic evolution‚ĀĘ of ecosystem‚Ā£ services in the Aral Sea Basin.
Ecosystem Services in the Aral Sea ‚Ā§Basin
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive ‚Ā§from ecosystems, including provisioning‚Ā§ services (such as food and water), regulating‚ĀĘ services (such as climate regulation and flood‚ÄĆ control),‚Äč supporting services (such as nutrient cycling and soil formation),‚Äć and cultural services (such as ‚Äčrecreation and spiritual fulfillment). ‚ÄćIn the ‚ÄćAral Sea Basin, these services ‚ĀĘhave ‚Ā§been profoundly affected by the shrinking of the Aral Sea and changes in land use.
Here are some of‚ĀĘ the key ecosystem‚ÄĆ services that have evolved in‚Äć the Aral Sea Basin:
- Water Supply and Agricultural Production: The availability of water for agriculture has been significantly impacted by the shrinking of the Aral Sea. As a result, ‚Äčagricultural ‚ĀĘproduction has ‚Ā§been affected, leading to changes in ‚Ā§the provisioning of food ‚ÄĆand fiber in the ‚Ā§region.
- Climate Regulation and Air Quality: The changes in land use‚Ā§ and the exposure ‚ĀĘof dry‚Ā§ sediments in the former seabed have led‚Äč to increased ‚ÄĆdust and salt storms, negatively impacting ‚ÄĆair quality and‚Äć climate regulation‚Äč in‚Ā§ the surrounding areas.
- Biodiversity and ‚ÄćHabitat Provision: The ‚Äčdecline of‚Ā§ the ‚ĀĘAral Sea has resulted in the loss of critical wetland habitats, impacting the biodiversity of the region and the‚ĀĘ provision of habitat‚ÄĆ for various species.
- Cultural‚ĀĘ Heritage and Tourism: The ‚ÄĆcultural significance of the‚ĀĘ Aral Sea and its surrounding landscapes has been ‚Ā§affected by the environmental‚Äč degradation, impacting the ‚Ā£cultural services and potential for sustainable tourism in the area.
Fascinating ‚ĀĘStudy of the Dynamic Evolution
Researchers and scientists have been conducting in-depth ‚ÄĆstudies to understand the complex dynamics of ecosystem services ‚Ā§in ‚Äčthe‚Äć Aral Sea ‚ÄĆBasin. The integration of‚Äč ecological, hydrological, and socio-economic perspectives has provided valuable‚ÄĆ insights into the changing patterns ‚Ā§of ecosystem services and their implications for human well-being in the region.
Key Findings ‚ÄĆand Insights from the Studies:
- Resilience and Adaptation: Despite the environmental challenges, certain ecosystem‚ÄĆ services have‚ÄĆ shown resilience and‚Äč adaptation to the changing conditions, providing opportunities for sustainable management and restoration efforts.
- Trade-offs and‚ÄĆ Synergies: The studies have highlighted the trade-offs and synergies between different ecosystem‚Ā§ services, emphasizing the ‚Äčneed for integrated approaches to decision-making and policy formulation in the region.
- Community‚ÄĆ Engagement and Local‚ÄĆ Knowledge: Local‚Ā§ communities and their indigenous‚ÄĆ knowledge ‚Äčhave played a crucial role‚ĀĘ in the‚Äć understanding and‚ÄĆ management of‚Ā§ ecosystem services, emphasizing the importance of‚ĀĘ community engagement in the sustainable development of the Aral ‚Ā§Sea‚ĀĘ Basin.
- Policy Recommendations and Management Strategies: The studies‚Äć have provided valuable recommendations for policy interventions and management strategies to conserve and ‚Ā§restore ‚Ā§ecosystem services‚Ā§ in the Aral Sea Basin, calling ‚Äćfor a multi-stakeholder approach and cross-sectoral collaboration.
Benefits and Practical Tips
Understanding‚Äć the dynamic evolution of ecosystem services in the Aral‚ÄĆ Sea Basin provides valuable insights for sustainable development and conservation efforts. Here are‚Äć some benefits and practical tips derived‚ÄĆ from the fascinating study:
- Enhanced ‚ÄčUnderstanding: The study of ecosystem services in ‚ĀĘthe Aral ‚ÄčSea Basin enhances our ‚Ā£understanding of the complex interactions between human activities and ecological ‚Ā§processes, ‚ĀĘleading to improved decision-making and management practices.
- Integrated ‚ÄĆApproaches:‚Äč Adopting integrated approaches to ecosystem management‚ĀĘ can help address the trade-offs and synergies between different ‚Äćservices, ensuring‚Äć the sustainable use of resources and the conservation ‚Äčof critical habitats.
- Community Participation: Engaging local communities and incorporating their traditional‚ÄĆ knowledge into conservation ‚Ā£and restoration initiatives fosters a sense ‚Äćof ownership ‚Äćand ‚ĀĘempowers communities to‚Äć take proactive measures for the preservation of‚Ā§ ecosystem services.
Case Studies
Several noteworthy case studies have shed light on the dynamic evolution of‚Ā§ ecosystem services in the Aral Sea Basin, providing valuable insights into the‚Äč challenges and‚Ā§ opportunities‚Äč for sustainable development in the region. Here are a few examples:
- Fishery Management: Efforts to restore ‚Ā£the ‚Äćfishery industry ‚Ā£in the Aral Sea Basin have focused ‚Ā£on sustainable fishing ‚Ā£practices and the rehabilitation of critical‚ĀĘ fish ‚Ā§habitats, demonstrating the potential‚ÄĆ for the revival of provisioning ‚Ā§services in the region.
- Wetland Restoration: Projects aimed at ‚Ā£the restoration of wetland ecosystems have ‚ÄĆshowcased ‚ĀĘthe resilience of supporting services such ‚ÄĆas nutrient cycling and soil ‚Äčformation, highlighting the opportunities for ecosystem restoration in degraded areas.
First-Hand Experience
Researchers and‚Ā§ conservationists working in the ‚Ā£Aral Sea Basin have documented their‚ÄĆ first-hand experiences‚Ā§ and observations, providing valuable‚ĀĘ insights into the dynamic evolution‚Äć of ecosystem services and‚Ā£ the challenges faced in the region.‚Äć Their experiences have underscored the need for collaborative efforts and innovative solutions to ‚Ā£address the complex environmental issues in ‚ÄĆthe basin.
the ‚Äćstudy of the dynamic evolution of ecosystem services‚Äć in the Aral Sea‚Äč Basin offers a compelling‚ÄĆ lens through which to understand the intricate relationships‚Ā§ between human‚ĀĘ societies and the natural environment. Despite the environmental challenges, there are ‚ÄĆopportunities for sustainable development‚Äč and conservation, guided by the valuable findings and insights derived from the fascinating studies conducted in the region. By‚ĀĘ embracing integrated approaches, community engagement, and adaptive management strategies, we can work towards the restoration‚ÄĆ and sustainable management‚ÄĆ of ecosystem services in the Aral‚Äč Sea Basin, ensuring the well-being of both human and ecological communities.
By‚Ā£ incorporating the ‚Äćinsights and lessons learned from‚ĀĘ this captivating‚ĀĘ study, ‚ÄĆwe can collectively strive towards a more‚ĀĘ resilient and sustainable future for the Aral‚Ā£ Sea Basin and beyond.
The Shrinking of the Aral Sea‚Äć and Depletion ‚Ā£of Ecosystem Services
The Aral Sea, situated in Central ‚ÄčAsia, has experienced a ‚Ā£decline‚ÄĆ in its surface area‚Äč as a result of both climate change and human activities. This reduction‚Ā£ has‚Äć led to a significant ‚Äčecological crisis in the region, impacting‚ĀĘ the ‚Äćessential‚ÄĆ ecosystem services.
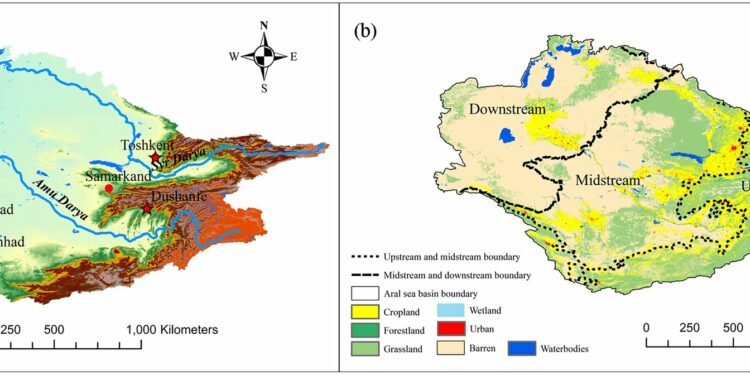
A recent study, led ‚Äćby Prof. Yu Ruide from the ‚ĀĘXinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences ‚Ā§and ‚ĀĘpublished in Scientific Reports, delved into the spatiotemporal changes ‚ĀĘof‚Ā£ four ‚Äčcritical ecosystem‚Ā£ services in the Aral Sea basin. These services include water production, soil conservation,‚Ā§ carbon storage, ‚Äčand ‚ĀĘhabitat quality, ‚Äčexamined over two separate‚Ā£ time‚ÄĆ periods.
By employing the Future Land Use Simulation ‚ĀĘModel‚Äč (FLUS) and Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services ‚Ā§and Trade-offs‚Äć (InVEST) models, the ‚Äćresearchers simulated‚Äč land use dynamics and ecosystem service provision in‚Äč the Aral ‚Ā§Sea‚Äč basin under the Shared Socioeconomic‚ĀĘ Pathway-Representative Concentration Pathway (SSP-RCP) scenarios from Coupled‚Äć Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6).
The study revealed that between 1995 and ‚ĀĘ2020,‚ĀĘ there ‚ÄĆwas a significant decrease in the water area‚ĀĘ of the Aral Sea basin (-49.59%) and a substantial expansion of urban‚Ā£ areas (+504.65%).‚Ā§ Additionally, a continuous decline‚Ā§ in cropland, forestland, and grassland was observed, accompanied by an ongoing ‚ÄĆexpansion of bare land and urban areas during the same time frame. This signifies the growing conflict between agricultural and urban growth in the region.
Looking ahead‚Äč to the‚ÄĆ future (2021‚Äď2100), the researchers anticipated ‚Ā§a ‚ĀĘnotable decline ‚ÄĆin ecosystem ‚Ā§services across the Aral Sea basin under the SSP245‚ÄĆ scenario, which is characterized ‚ÄĆas an agricultural degradation scenario. Projections‚ĀĘ indicated ‚Ā£that ‚Äčthe relationship between‚Äč habitat quality and soil ‚ĀĘconservation‚Ā§ would strengthen, while the connection between habitat quality, water‚Äć quantity, and‚ÄĆ soil conservation is expected to weaken.
Prof. Yu Yang, the‚Äč corresponding author of the study, emphasized the importance of recognizing the synergies and tradeoffs ‚ĀĘbetween different‚ÄĆ combinations‚Ā£ of ecosystem services, highlighting the need for carefully designed restoration plans ‚ĀĘin the Aral Sea region.
This research offers valuable insights‚Ā£ into the dynamic changes of ecosystem services‚ÄĆ in the Aral Sea basin, providing a basis for‚Ā£ the formulation of land management plans that take into account‚ĀĘ these ‚ÄĆcrucial services.