Researchers Unveil New Insights‚Ā§ into Mercury’s Magnetosphere Using BepiColombo Flyby Data
Introduction to Mercury’s Mysteries
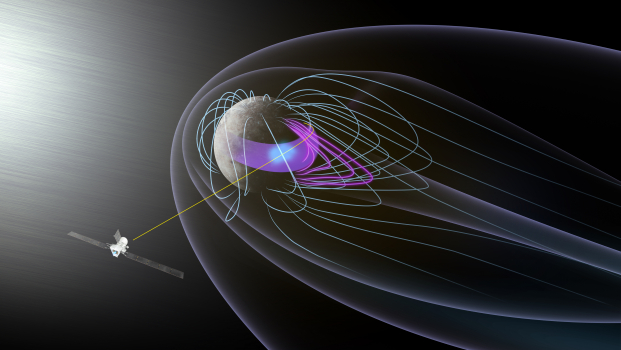
Mercury, ‚Ā£the‚ĀĘ closest‚Äć planet to the Sun, has ‚Äćlong intrigued scientists due ‚Ā§to its‚Äč unique ‚Ā£characteristics‚Ā£ and extreme ‚Ā§environment. The‚Äć recent flyby of NASA‚Äôs BepiColombo spacecraft has provided unprecedented data that‚Ā£ sheds light on the‚Ā£ planet’s magnetosphere, revealing features and phenomena previously masked by limited observational capabilities.
Breakthroughs from BepiColombo’s Discoveries
Launched ‚ĀĘin 2018 with a‚ĀĘ mission to‚Ā£ study Mercury closely, BepiColombo made a significant pass near Venus and gathered valuable data. This mission is pivotal ‚Äćas‚Ā£ it‚ÄĆ allows‚Äć researchers to analyze magnetic ‚ÄĆfield interactions‚Ā§ that ‚Ā£shape Mercury‚Äôs environment. The findings from this flyby ‚Äćcontribute crucial insights into how solar winds interact with ‚Äćplanetary atmospheres.
Key Findings
- Magnetic Field Interactions: Early analyses indicate complex interactions‚Äć between solar‚Ā§ particles and Mercury’s magnetic field. These ‚ĀĘexchanges are believed‚Ā§ to create transient structures within the magnetosphere.
- Unexpected‚Äč Variations:‚Äć The observations revealed ‚Ā§surprising variations in ‚Ā£magnetic strength during different phases of the spacecraft‚Äôs journey, suggesting dynamic changes within Mercury‚Äôs magnetic environment.
What ‚ĀĘis the significance of the BepiColombo‚ĀĘ mission for understanding planetary habitability?
“`html
Unlocking Mercury’s Secrets: Scientists Reveal Hidden ‚ĀĘMysteries ‚Ā§of the‚Äč Planet’s Magnetosphere Using BepiColombo Flyby Data
The exploration of Mercury, the solar system’s innermost planet, has long fascinated‚Äč scientists. With advancements in‚ÄĆ space technology, the BepiColombo mission provides groundbreaking insights ‚ÄĆinto Mercury’s magnetosphere, unveiling‚Ā£ secrets that have remained hidden for decades. In this article, we dive deep into the‚ÄĆ findings derived ‚ĀĘfrom‚Äč BepiColombo’s flyby‚Äć data, enhancing our understanding of Mercury’s complex magnetic environment.
The ‚ÄčBepiColombo Mission: A Brief Overview
BepiColombo, a‚ĀĘ joint mission by the European Space Agency (ESA)‚Ā£ and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), was launched to study ‚ĀĘMercury and its magnetosphere comprehensively. This mission primarily aims to:
- Investigate Mercury’s geology and internal structure.
- Understand the dynamics of its magnetosphere.
- Explore the interaction between solar wind and Mercury’s magnetic‚Äć field.
The spacecraft is named after Giovanni Battista Giuseppe ‚Äč”Bepi” Colombo, the Italian scientist‚ĀĘ who significantly contributed to our understanding of Mercury.
Significance of Mercury’s ‚ĀĘMagnetosphere
Mercury possesses a unique magnetic field compared to other terrestrial planets. Despite its small size, ‚ÄĆits magnetosphere ‚Ā£plays a crucial role in shaping the planet’s environment:
- Protection from‚Ā£ Solar Radiation: Mercury’s magnetosphere shields ‚Äćits surface from harmful solar particles, making it a vital factor in understanding planetary habitability.
- Geological Activity: ‚Äć The interaction between the solar wind and Mercury’s magnetic field is key ‚Äčto deciphering geological activities, including tectonic features and volcanic ‚ÄĆhistory.
- Planetary Atmosphere: Studying ‚Äčthe magnetosphere helps‚ÄĆ scientists gather insights into Mercury’s thin exosphere, composed mainly ‚Ā£of oxygen, sodium, and potassium.
- Instrument‚Ā£ Advancements: Equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, ‚ĀĘBepiColombo is tailored specifically for studying the intricacies of planetary magnetospheres‚ÄĒan upgrade over previous missions which had limited instruments for such analyses.
Implications for Future Research
The information garnered from this ‚Ā§flyby ‚Äčwill ‚Ā§not only enhance our‚Ā§ understanding of Mercury but ‚ÄĆalso‚ÄĆ provide broad implications for comparative planetology ‚Äč‚ÄĒ understanding‚Äč other ‚ÄĆcelestial ‚Äčbodies with similar characteristics across our solar system and even beyond.
Expanding Knowledge Beyond ‚ĀĘLocal Observations
In addition, ongoing assessments may guide future missions directed ‚ĀĘtowards ‚ĀĘplanets like Mars or exoplanets exhibiting magnetospheres ‚ÄĆinfluenced ‚ÄĆby their stars‚Äô radiation patterns. ‚Äć
Conclusion: Looking Ahead
NASA’s commitment through projects like BepiColombo exemplifies our quest for knowledge about planetary ‚Äčsystems. Each revelation ‚Äčopens‚Ā§ new pathways for research ‚Ā§inquiries that‚ÄĆ could redefine what we know about planets‚Äć in our ‚ĀĘsolar neighborhood.
With each‚Äć passing event captured by instruments aboard cutting-edge spacecrafts such as BepiColombo, we inch‚ĀĘ closer toward unraveling many celestial‚Äć mysteries‚Äć ‚ÄĒ expanding both scientific knowledge and public fascination regarding ‚Äčour cosmic surroundings.