Exploring the Legacy‚ÄĆ of the ‚Ā£Hubble Space Telescope
A Milestone in Space Observation
The Hubble Space Telescope has been at the forefront ‚Äčof astronomical research for more than 30 years, consistently ‚Äćcontributing to pivotal discoveries that enhance our ‚Äčcomprehension of the cosmos. This‚ĀĘ remarkable instrument ‚Äćstands as a testament to global‚Äć collaboration, involving joint ‚Äćefforts between NASA and the ‚ÄĆEuropean‚ĀĘ Space Agency ‚Äć(ESA).
Collaborative Management Efforts
What role do jet streams‚ĀĘ play in the dynamics of ‚Ā£the Great Red Spot?
“`html
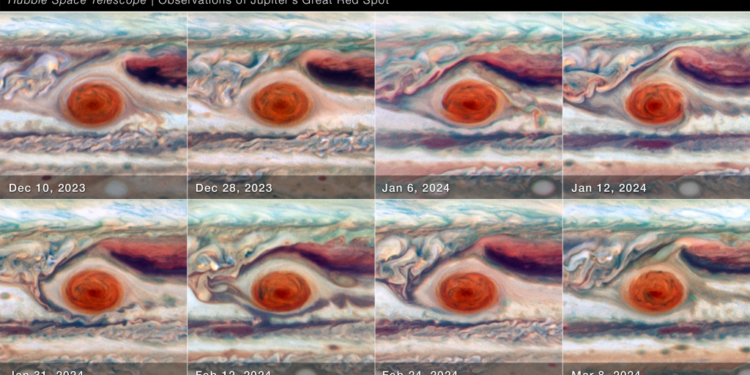
NASA’s Hubble Sees Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Squeeze and Stretch Like a ‚ĀĘStress Ball!
Understanding Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
Jupiter‚Äôs Great‚Ā£ Red Spot is a spectacular feature of the solar system. This massive ‚Ā£storm, larger than Earth, has fascinated astronomers and space enthusiasts ‚ÄĆalike since‚ÄĆ its discovery over 350 years‚Äč ago. But recent observations by NASA’s‚Ā£ Hubble Space Telescope have revealed something even more intriguing: the‚Äć Great Red Spot is not static; ‚Ā§it‚ÄĆ appears to squeeze and stretch much like a‚Ā§ stress ball!
The‚Ā£ Latest ‚ÄćObservations by ‚ÄĆthe Hubble‚Ā§ Space Telescope
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope‚ÄĆ has ‚Äčprovided stunning visuals of Jupiter and its Great Red Spot, ‚Äćshowcasing its dynamic nature. These ‚Äćobservations ‚ÄĆhave ‚ÄĆindicated changes ‚ĀĘin size, shape, and color as ‚ĀĘthe storm continually evolves.
- Size Fluctuations: Hubble’s recent data indicates that the Great Red‚Ā£ Spot has been decreasing in size over the ‚Ā§past century.
- Color Changes: Observations show that ‚Ā£the storm’s rich ‚Ā§crimson hue varies, ‚Äćoften showing a more orange ‚Ā£or beige tone during its‚Äč stretching phases.
- Wind Patterns: The Great Red Spot’s wind‚Ā§ speeds and direction appear to fluctuate, aiding‚ĀĘ in its unpredictable behavior.
What Causes ‚Ā£the‚ÄĆ Squeeze and Stretch of the Great Red Spot?
The ‚Ā§squeezing ‚Ā§and stretching motions of Jupiter’s‚ĀĘ Great Red‚Ā£ Spot can be ‚Ā£attributed to ‚ĀĘa combination of atmospheric dynamics and gravitational influences. Scientists believe that:
- Jet Streams: Strong jet streams ‚ÄĆsurrounding the storm play a pivotal role in its‚ĀĘ shape and‚ĀĘ size. Changes in these currents can cause the storm to elongate or compress.
- Internal ‚ÄĆEnergy: The storm‚Äôs immense energy sourced from the ‚Äćplanet‚Äôs heat‚Äč contributes to its changing structure.
- Environmental ‚Ā§Factors: Interactions with smaller storms and weather‚Äč systems nearby‚ÄĆ can influence the Great Red Spot
The management of Hubble’s operations is overseen by NASA’s‚Ā£ Goddard Space Flight Center located in Greenbelt, Maryland. In addition, Lockheed‚ÄĆ Martin Space in‚Äč Denver plays a significant role in supporting mission operations‚Äć from Goddard.‚ÄĆ Further enriching this intricate network is the esteemed Space Telescope Science Institute situated in Baltimore, Maryland. Operated by the Association of‚Ā§ Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), this institute is tasked with overseeing all scientific operations related to Hubble ‚ĀĘunder NASA‚Äôs guidance.Continuing Impact and Discoveries
Hubble‚Äôs contributions extend beyond individual findings; it has transformed our understanding across various ‚ĀĘdomains of ‚Ā£astronomy‚ÄĒfrom determining the rate‚Äč of expansion of galaxies to uncovering details about‚ĀĘ distant exoplanets. For‚Äč example, recent studies‚Ā§ utilizing data from Hubble have provided new insights into dark matter‚Ā§ interactions, revealing how galaxies ‚Ā£evolve over billions of years. With its ability to capture breathtaking visuals and essential data ‚Ā£about our universe, Hubble ‚Ā§remains an irreplaceable tool for‚Äč scientists around the‚ĀĘ globe.
As‚ĀĘ technology advances and we look ‚ÄĆtoward future telescopes like James Webb, which launched recently with a different observational focus yet aims to build upon findings initiated‚Äč by Hubble, one thing remains clear: The legacy ‚Äčestablished by Hubble continues to influence contemporary astrophysics profoundly.