Reassessing the Value of Ecosystem Services: Trends and Insights
Understanding Ecosystem Services and Their Importance
Ecosystem services encompass the many benefits that natural environments provide to society. These services are crucial for maintaining ecological balance, supporting human life, and fostering economic development. As global challenges like climate change escalate, understanding these services’ value becomes increasingly essential.
One foundational work on this topic is from Costanza et al. (1997), which estimated the total annual value of Earth’s ecosystem services at approximately $33 trillion—an amount that has likely increased since then due to evolving ecosystems and developments in valuation methods (Costanza et al., 1997). Subsequent research by Xie et al. (2015) has emphasized regional assessments in specific nations such as China, showcasing the significant monetary contributions made by various ecosystems.
Recent Advances in Valuation Methodologies
In recent years, there have been strides in refining the methodologies used to quantitatively assess ecosystem service values. For instance, Xie et al. (2015) improved upon existing frameworks by introducing unit area value equivalents tailored to varied geographic contexts. This enhancement allows for more accurate valuations across different ecosystems while accounting for local socio-economic conditions.
Moreover, innovative studies like those conducted by Wang et al. (2019) emphasize the unique characteristics of karst landscapes in China—demonstrating how landscape-specific parameters can influence both ecology and economics.
The Role of Land Use Change
Land use changes significantly impact ecosystem service offerings; thus it is a pressing topic of study within environmental science. Fu & Zhang (2014) outline contemporary concepts around land use modification alongside methodologies necessary for evaluating its implications on service provision.
Critical insights into this relationship were demonstrated through Huang et al.’s recent work integrating socioeconomic factors with territorial patterns into assessments of ecosystem service values published in 2023—their findings offered fresh perspectives on how developmental policies might improve or degrade these values over time.
Case Studies from Diverse Regions
“`html
</p>
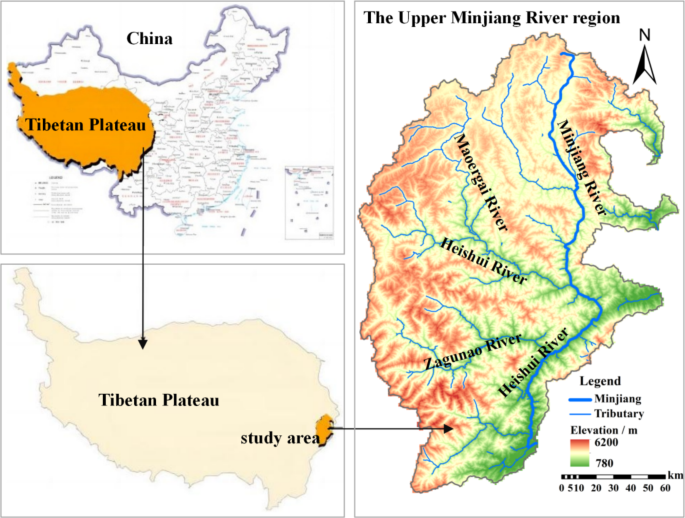
Unraveling the Dynamic Changes and Influential Forces Behind Ecosystem Service Value in China’s Upper Minjiang River
Understanding Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, playing a crucial role in sustaining human life and well-being. These services can be broadly categorized into four main types:
- Provisioning Services: These include the supply of food, water, timber, and fiber.
- Regulating Services: These services regulate ecosystem processes, such as climate regulation, flood mitigation, and water purification.
- Supporting Services: Services that maintain the conditions for life, such as soil formation, nutrient cycling, and primary production.
- Cultural Services: These are non-material benefits, such as recreational, aesthetic, and spiritual enrichment.
The Importance of Upper Minjiang River Ecosystem Services
The Upper Minjiang River in Sichuan Province is a vital resource, providing essential ecosystem services that support local communities and biodiversity. Changes in land use, climate, and human activities have been affecting these services, leading to a pressing need for comprehensive evaluation.
Key Factors Influencing Ecosystem Service Value
Understanding the dynamics affecting ecosystem service value requires a deep dive into several influential factors:
- Natural Factors:
- Climate Change: Alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt natural processes and habitats.
- Urban Agglomerations: In an analysis examining spatial responses during urbanization phases conducted by Yu et al., alterations were identified wherein increasing population density directly affected regional ecological footprints.
- Wetlands: Song et al.’s study focused on Northeast China’s wetlands revealed dynamic shifts characterized by changing climate conditions driving variability within ecosystem service valuations outputted from these bio-rich zones.
- Mountain Regions: Investigations into mountainous areas have showcased resilience—a finding captured when Liu’s team documented habitat modifications triggered primarily due to anthropogenic pressures against rapid environmental changes observed along river basins across Qinghai Province (2022).
Implications for Policy-Making and Restoration Efforts
Understanding varying factors influencing biodiversity provides essential insights necessary for developing effective conservation policies aimed at sustainable resource management strategies applicable across regions experiencing significant ecological stressors such as pollution or habitat loss—critical elements highlighted through multiple studies addressing systemic relationships among environment-health-economy interactions.
Research endeavors focusing upon integrative restoration initiatives note synergies emerging between efforts toward restoring lost habitats coupled with adopting ecolabeling mechanisms designed to raise public awareness regarding consuming sustainably sourced products derived via responsible agricultural practices illustrated notably throughout various landscapes including coastal ecosystems assessed over recent decades yielding positive community-level socio-economic impacts confirmed through comprehensive monitoring schemes established during restoration projects initiated post-disaster recovery tasks performed nationwide outlined extensively via Zhang’s comprehensive evaluation metrics analysis released earlier last year depicting overall rejuvenation narratives leading toward gradual sustainability transitions achievable when articulated intelligently across governance fronts effectively promoting relevancy amongst stakeholders entrusted with directory responsibilities allocated towards both economic upliftment intertwined intricately alongside ecological preservation commitments signifying profound advancements anticipated forthcoming tenures ahead aimed firmly encased within best-practice frameworks outlined strategically coordinated harmoniously realized internationally built networks fostering shared-results systematically aligned pursuing unified goals stemming evidently strengthened collaborative commitments directed responsibly while espousing conscientious artworks prevalent today ensuring rightful stewardship alongside progressive growth fusing seamlessly founded partnerships forged along sustainable development trajectories unfinished yet ripe continually ever-expanding our oceans’ depths selvedged their myriad greater glories waiting earnestly awaiting us!