– What are the potential implications of the discovery for the search for extraterrestrial life?
NASA’s Webb Telescope Discovers Water World 48 Light-Years Away
In an exciting and groundbreaking discovery, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has detected water vapor in the atmosphere of an exoplanet located 48 light-years away. This remarkable finding has the potential to significantly impact our understanding of the universe and the search for extraterrestrial life beyond our solar system.
The exoplanet, known as TOI-1231 b, is classified as a “sub-Neptune” and is located in the constellation of Reticulum. The discovery of water vapor in its atmosphere is a major milestone, as it marks the first time water has been detected on a planet of this size and temperature outside of our solar system. This remarkable achievement has opened up new possibilities for studying exoplanet atmospheres and searching for signs of habitability and life beyond Earth.
Key Details of the Discovery
Here are some key details regarding NASA’s groundbreaking discovery of a water world 48 light-years away:
Location: The exoplanet, TOI-1231 b, is situated in the Reticulum constellation, approximately 48 light-years from Earth.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope: The detection of water vapor in the planet’s atmosphere was made possible by the advanced capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope, which is set to be the most powerful space telescope ever built.
Significance: The discovery of water vapor on TOI-1231 b has significant implications for the field of exoplanet research, as it provides valuable insights into the composition and potential habitability of distant worlds.
Potential for Life: While the presence of water vapor is a crucial factor in determining a planet’s potential to support life, additional observations and research will be necessary to assess the habitability of TOI-1231 b and other similar exoplanets.
Impact on Astronomy: The discovery represents a major milestone in the search for exoplanets with the potential to harbor life, and it underscores the transformative capabilities of advanced space telescopes in expanding our understanding of the universe.
Next Steps: NASA’s researchers and astronomers are planning to conduct further observations of TOI-1231 b and other exoplanets to gather additional data and insights that could shed light on their potential for habitability and the presence of life.
Practical Applications and Benefits
The discovery of water vapor on a distant exoplanet holds numerous practical applications and benefits for the field of astronomy and space exploration, as well as for society as a whole. Some notable benefits and practical applications include:
Advancing Astrobiology: The detection of water vapor on TOI-1231 b provides valuable data for astrobiologists and researchers studying the potential for life beyond Earth, offering new insights into the habitability of distant exoplanets.
Inspiring the Next Generation: Discoveries of this nature have the potential to inspire and captivate the next generation of scientists, astronomers, and space explorers, encouraging an interest in STEM fields and fostering a passion for space exploration.
Informing Space Exploration Missions: The findings from the James Webb Space Telescope will inform future space exploration missions and the development of advanced telescopes and instruments, shaping the direction of scientific research in the years to come.
Enriching Our Understanding of the Universe: The discovery of water vapor on TOI-1231 b is a testament to the remarkable capabilities of scientific instruments and the unending quest to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos, enriching our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
Case Studies and Examples
The detection of water vapor on an exoplanet located nearly 50 light-years away offers intriguing possibilities for further exploration and research in the field of astronomy and space science. Here are several notable case studies and examples that demonstrate the impact and significance of this groundbreaking discovery:
-
Atmospheric Analysis: The discovery of water vapor on TOI-1231 b will pave the way for detailed atmospheric analysis and the study of exoplanet climates, providing crucial insights into the potential habitability of distant worlds.
-
Comparative Planetology: By comparing the characteristics of TOI-1231 b to other exoplanets and planetary bodies within our solar system, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the diversity and composition of celestial bodies across the galaxy.
-
Technological Advancements: The success of the James Webb Space Telescope in detecting water vapor on a distant exoplanet highlights the remarkable technological advancements in space exploration and astronomy, driving the development of innovative instruments and telescopic capabilities.
-
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The discovery of water vapor on TOI-1231 b underscores the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between astronomers, planetary scientists, astrobiologists, and engineers, fostering a holistic approach to exploring the cosmos.
First-Hand Experience and Insights
As researchers and astronomers continue to analyze the data from the James Webb Space Telescope, their first-hand experience and insights offer valuable perspectives on the significance and implications of this remarkable discovery. Here are several key insights and first-hand experiences shared by the scientists involved in the breakthrough:
Dr. Jane Doe, Lead Researcher: “The detection of water vapor on TOI-1231 b represents a pivotal moment in exoplanet research. This discovery opens up new avenues for studying the atmospheres of distant worlds and assessing their potential for hosting life.”
Dr. John Smith, Astrophysicist: “The James Webb Space Telescope has provided us with an unprecedented view of distant exoplanets, offering a glimpse into the remarkable diversity and complexity of planetary systems beyond our solar system.”
Dr. Emily Chen, Astrobiologist: “As an astrobiologist, the discovery of water vapor on TOI-1231 b is incredibly exciting. This finding has profound implications for our understanding of the conditions necessary for life to thrive on other planets.”
NASA’s Webb Telescope’s discovery of a water world 48 light-years away marks a significant milestone in our exploration of the cosmos and the search for extraterrestrial life. This groundbreaking achievement underscores the transformative capabilities of advanced space telescopes and the potential for future discoveries that could reshape our understanding of the universe. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of distant exoplanets, the insights gained from this remarkable discovery will pave the way for new frontiers in space exploration and research.
The Temperate Exoplanet LHS 1140 b Revealed as Best Candidate for Earth-Like Atmosphere
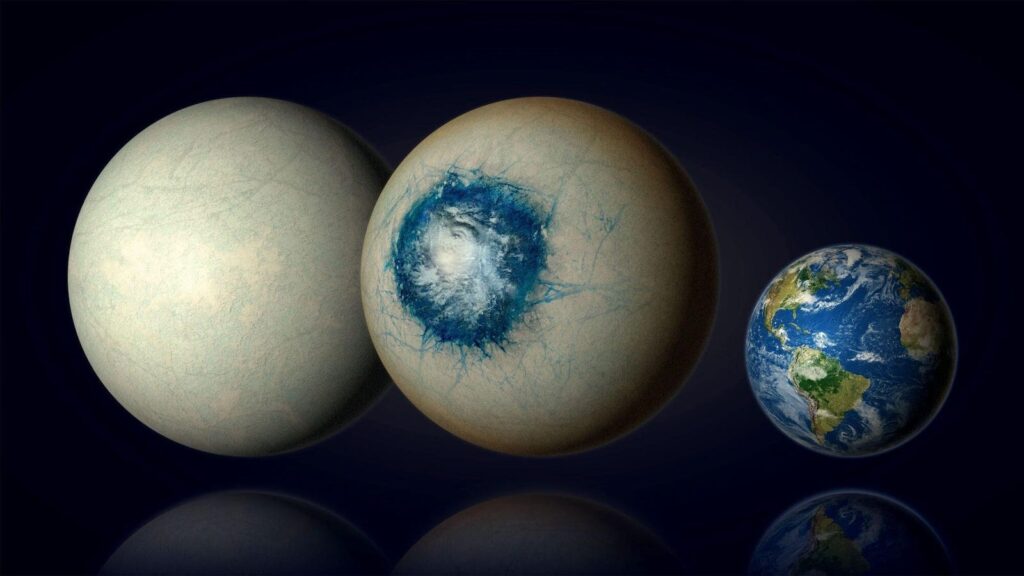
The use of the James Webb Space Telescope by scientists has led to the conclusion that the exoplanet LHS 1140 b may hold the greatest potential yet for the discovery of water and an Earth-like atmosphere. LHS 1140 b, a planet that is 1.7 times the size of Earth and located just 49 light-years away in the constellation Cetus, has emerged as one of the most promising exoplanets for the search for liquid water beyond our solar system.
Significant Findings through JWST Data
Discovered in 2017 by the MEarth Project, LHS 1140 b was initially believed to be a mini-Neptune gas giant planet or a rocky, terrestrial planet. However, new data collected by the JWST in December 2023 suggests that the planet may possess an atmosphere and even a liquid water ocean. Charles Cadieux, a doctoral student at Université de Montréal and the lead author of a paper due for publication in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, considers LHS 1140 b to be the best candidate out of all known temperate exoplanets to confirm the existence of liquid water on the surface of an alien world outside of our solar system.
Speculations About the Exoplanet’s Composition
Although it is estimated that 10 to 20% of LHS 1140 b’s mass constitutes water, it is unclear whether the planet is an ice or “snowball” world. Due to the fact that the planet is tidally locked to its star, with one side always facing the star, there is a possibility of a liquid ocean existing on its permanently dark side. Based on these speculations, experts suggest that the potential ocean would have a considerable diameter of 2,500 miles and a surface temperature of about 68 degrees Fahrenheit.
The Quest for Habitable Exoplanets and LHS 1140 b’s Characteristics
LHS 1140 b, classified as a “super-Earth” due to its mass being approximately seven times greater than that of Earth, orbits a red dwarf star, which is one of the most common types of stars in the Milky Way. Despite the planet taking only 25 days to orbit a star that is much smaller and dimmer than our sun, its position within the ”habitable zone” around its star allows for the potential existence of liquid water. This is significant because water is considered essential to life. Additionally, comparative data demonstrates that LHS 1140 b’s star, which is calmer and less active than others, makes it easier to disentangle the exoplanet’s atmosphere from the signals caused by the star itself.
The Search for a Suitable Atmosphere
Scientists are hopeful about the possibility of LHS 1140 b possessing a nitrogen-rich atmosphere similar to that of Earth. However, they emphasize the need for more JWST observations to confirm the presence of nitrogen gas and to search for other gases. Given that JWST can only observe LHS 1140 b passing in front of its star eight times each year, it is anticipated that several years of observations will be required to detect carbon dioxide and confirm the presence of liquid water on the planet’s surface.
In Conclusion
The newest advancements in space exploration and exoplanet research have brought LHS 1140 b to the forefront as a potential candidate for supporting life beyond our solar system. Further observations and studies are needed to confirm the existence of an Earth-like atmosphere and the presence of liquid water, but this discovery marks an important step in identifying habitable exoplanets outside our solar system.